[GNU Manual] [No POSIX requirement] [Linux man] [FreeBSD man]
Summary
hostid - print numeric host identifier
Lines of code: 94
Principal syscall: write() (via printf())
Support syscalls: None (gethostid() is not a syscall)
Options: 2 (help and version)
Added to Shellutils in September 1997 [First version]
Number of revisions: 63 [Code Evolution]
- None
error()- Outputs error message to standard error with possible process termination
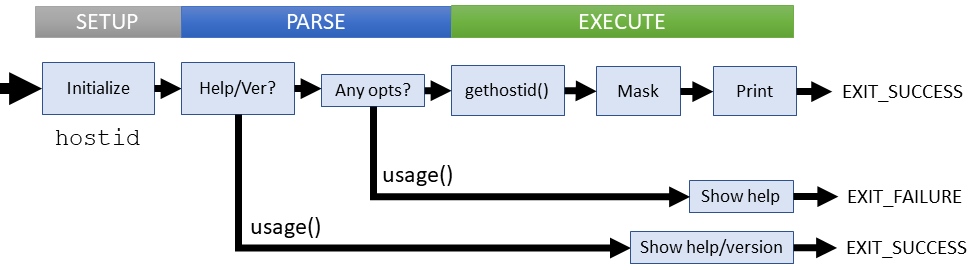
Setup
hostid only uses the default parsing options, which require no initialization
main() initializes one local variable, *ip, to hold the expected 32-bit integer returned from gethostid()
Parsing
Parsing for hostid involves two checks:
- Check for any long options
- Check for anything else
Parsing failures
Thess failure cases are explicitly checked:
- If any non-long option is passed
- If any argument is passed
This failure result in a short error message followed by the usage instructions.
Execution
Call the system-specific gethostid() function (usually in unistd.h). Mask the lower 32-bits and print the result.
The hostid is typically found in /etc/hostid. Otherwise, it may be generated from another system property, such as a local IPv4 address.
Execution will not fail, even if gethostid() returns something unusual